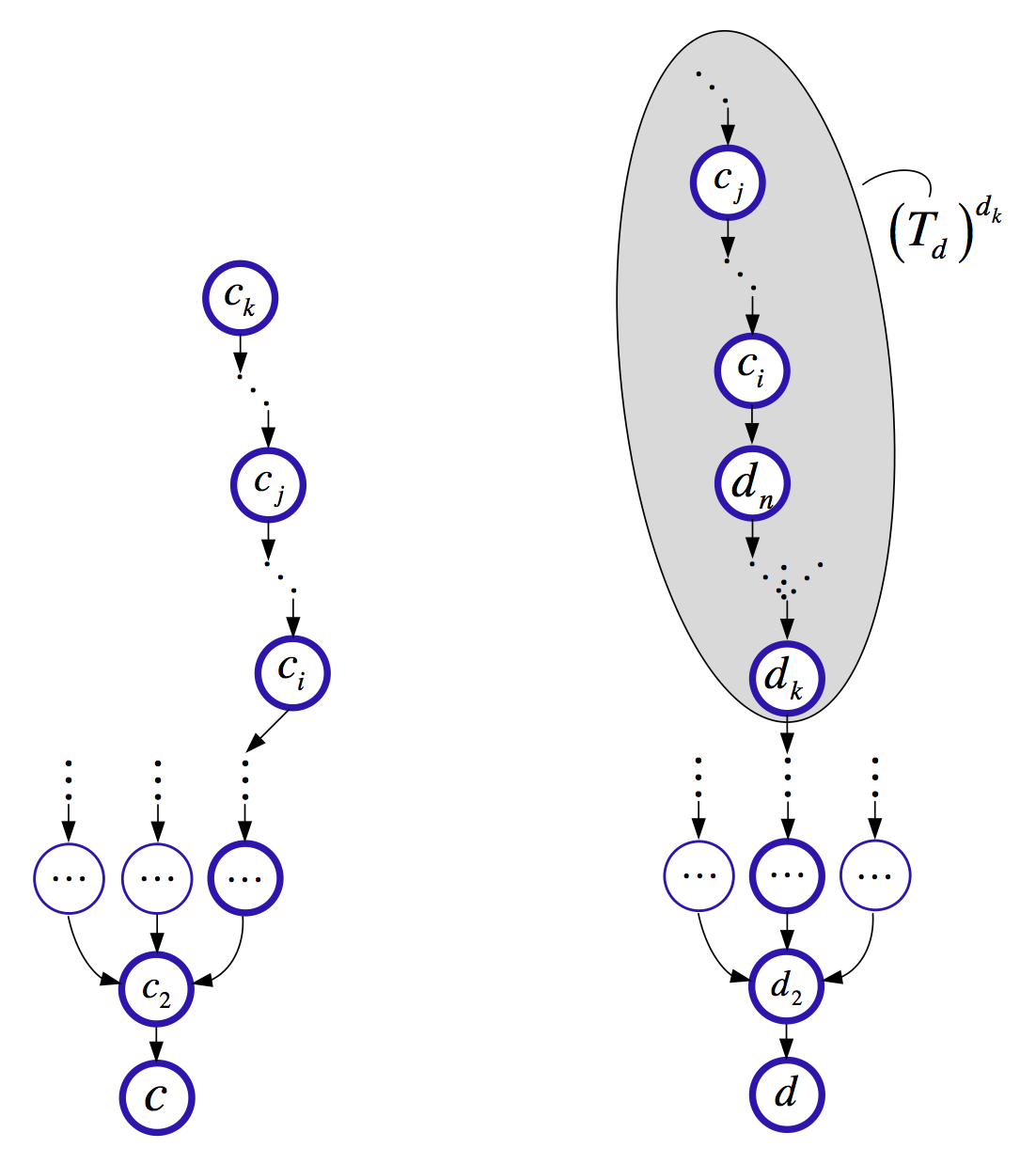
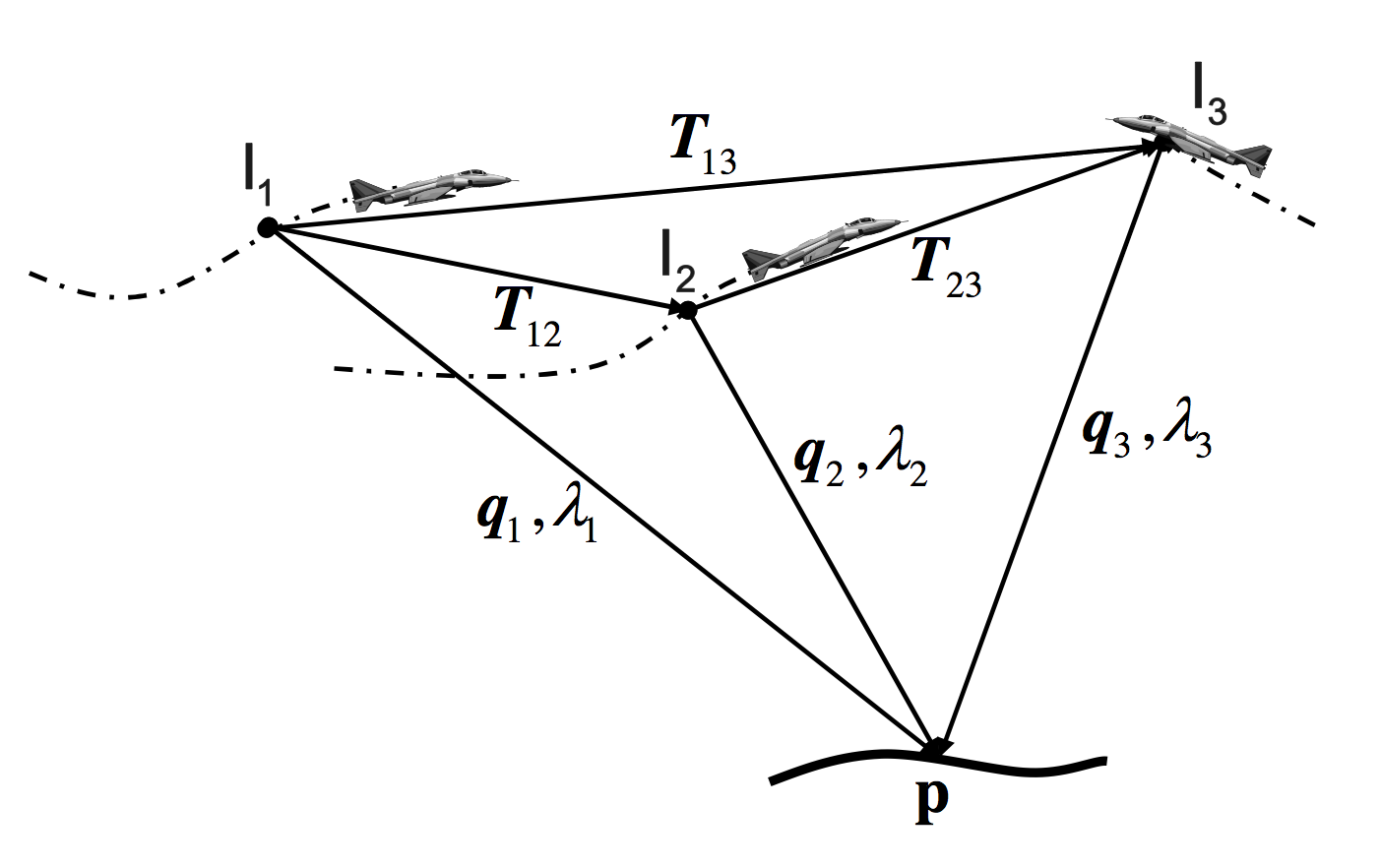
A multi-agent scenario is considered, in which the different robots share information to improve navigation and extend sensing. A graph-based approach was developed to guarantee a consistent information fusion between the different robots assuming a general multi-robot measurement model. Using the graph structure, separately maintained by each robot, appropriate correlation terms are calculated upon-demand and used within the update step of the filter. The method (see IJRR2012) is also applicable to implicit measurement models and in particular when using three-view geometry constraints (more details). Such an approach was developed in RAS2012, where the three-view constraints are applied whenever the robots observe a common scene. One thing to note is that the scene does not necessarily have to be observed by the robots at the same time.
A consistent decentralized data fusion (DDF) is studied within the smoothing and mapping framework as well (see ICRA2013). Here, the robots share certain variables of choice, such as observed 3D points, to both extend sensing horizon and improve localization and mapping. Consistent information fusion is guaranteed by explicitly avoiding using the same observation more than once (i.e. double counting), via information down-dating that is expressed in graphical models by anti-factors. Information summarization techniques are developed to efficiently retrieve the probabilistic information to-be-shared from the local factorized joint probability distribution, represented by the Bayes net.